Full compatibility testing process involves ABO and RhD (Rh factor) typing; screening for antibodies against other blood group systems; and crossmatching, testing the recipient’s blood plasma against the donor’s red blood cells.
Compatibility Testing
This is the procedure of providing compatible red cells for transfusion either by serological testing or electronic issue.
Compatibility testing – Test directoryGroup and Antibody screen (Group and Save)
A valid group and save is required to determine the ABO and antibody status prior to the issue of blood products such as red blood cells, platelets and plasma.
ABO testing involves testing a person’s red cells for the presence or absence of A and/or B antigens and testing the same person’s plasma for the presence or absence of anti-A and anti-B antibodies.
Antibody screen/detection is a test used to demonstrate the presence of clinically significant alloantibodies (capable of causing haemolytic transfusion reactions or haemolytic disease of the foetus/newborn).
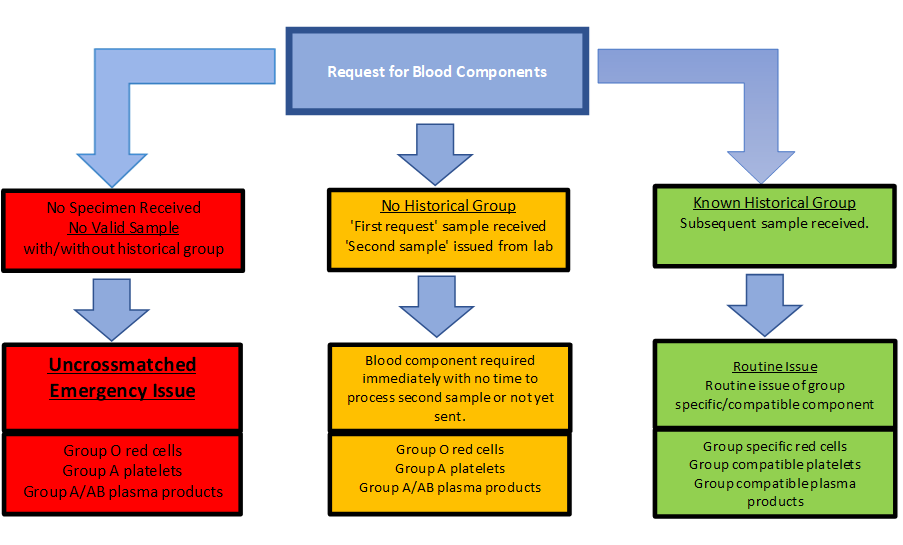
Compatibility testing – Antibody screenThe laboratory requires two Group and Save specimens taken a minimum of 12 hours apart to provide group specific blood components.
Where this cannot be achieved and blood is required within 12 hours, the laboratory will provide a “second sample” a sample tube that can only be released from the Transfusion laboratory once the primary specimen has been received. This sample must be then taken under the same conditions as any other group and save sample and returned to the lab for urgent processing.
If blood is required before the second sample can be processed the lab will consider a concessionary release of blood components provided the request meets certain criteria. Deviating from normal policy requires justifiable authorisation as soon as practicable.